SEO is one of the most lucrative marketing channels you can invest in 2021.
Do it right, and you’ll have qualified buyers lining up for your product/service every month without having to spend a single dollar in ads.
But how do you do it right?
There are thousands of guides, articles, training, and courses on the topic, so it’s very easy to get overwhelmed.
Where do you even start with your B2B SEO?
Well, that question led us to creating this guide.
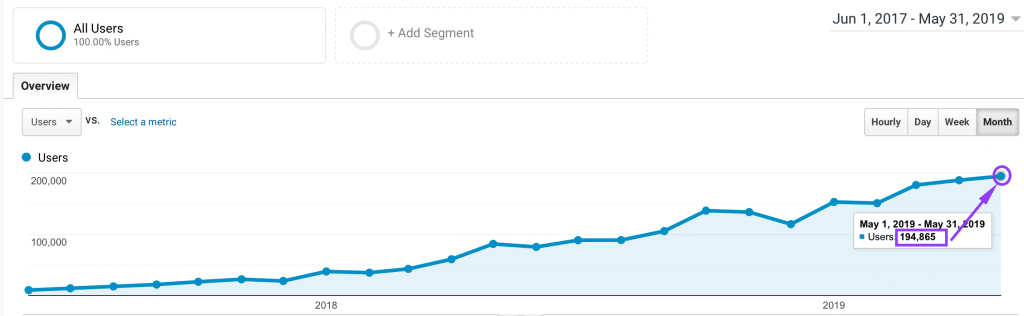
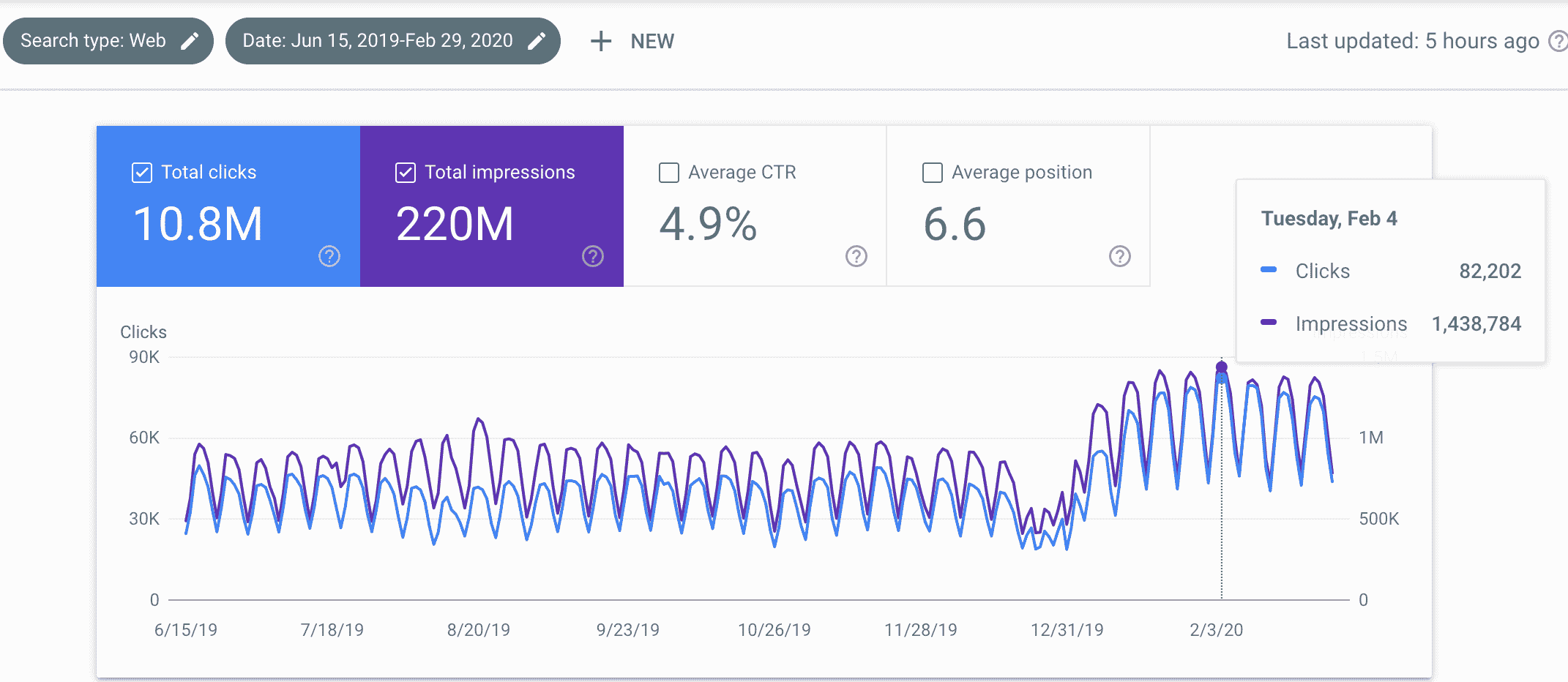
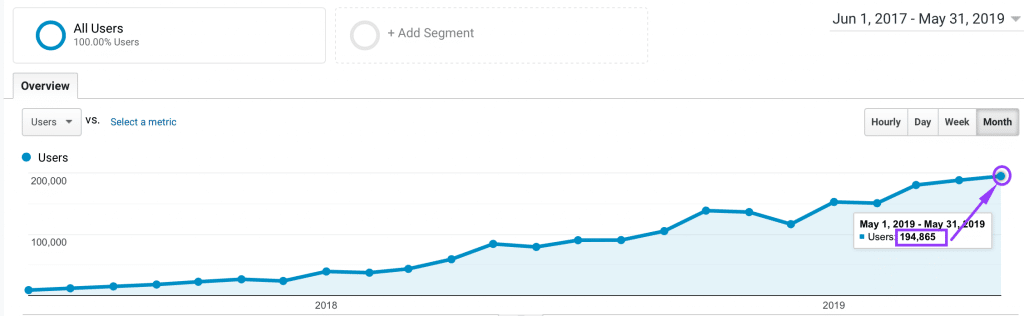
At Apollo Digital, we have a TON of experience with B2B SEO. We’ve helped several of our B2B clients go from 0 to 200,000 monthly organic traffic with our proven, step-by-step SEO process.
And in this guide, we’re going to spill the beans on what, exactly, we do to get such results.
Everything we’re going to cover here is super practical and step-by-step, so all you’ll have to do is implement what we teach you, and you’re on your way to getting insane results.
Here’s what we’re going to cover:
- B2B SEO Basics - Everything you need to know to get started.
- B2B vs B2C SEO. What’s the difference, and how it matters.
- The SEO Formula, or, how Google decides what ranks, and what doesn’t.
- Our 6-step process for doing B2B SEO (and getting our clients to 200,000+ monthly organic traffic).
- B2B SEO Case Study - Step-by-step case study on how we grew a B2B client from 0 to 200,000 monthly organic traffic with SEO.
- B2B SEO FAQ (to answer any questions you might still have).
So, let’s get started.
B2B SEO 101
Before we can teach you how to do B2B SEO, we’re going to cover some basics.
If you’ve already dabbled in SEO, just click here to skip ahead.
Otherwise, here we go:
SEO, in a nutshell, is the process of reaching your target audience by ranking for search phrases on search engines like Google.
B2B SEO, on the other hand, is pretty much the same thing, with the only difference being that your target audience is decision-makers in organizations. For example:
- A CEO founder looking for a “project management software”
- A CMO searching for “CRM tools”
- An HR manager searching for “employee onboarding checklist”
And so on.
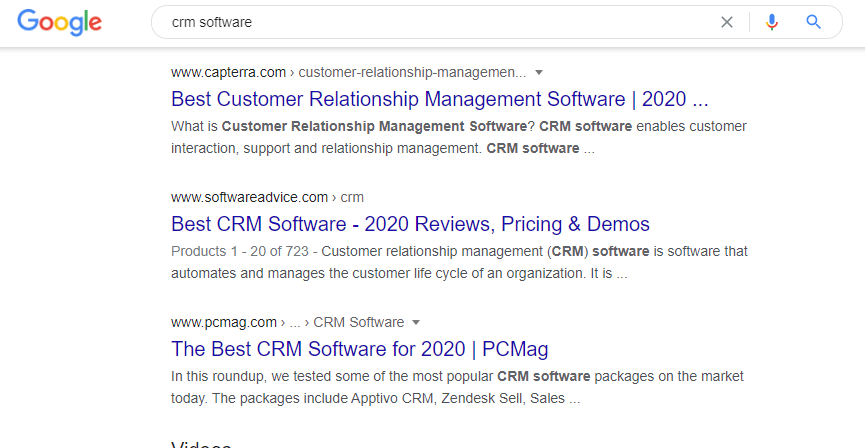
To make this more clear, let’s say, for the sake of the example, you’re selling a B2B CRM software. Meaning, you’re selling software for managing leads.
You’d want to rank for direct intent keywords (i.e. keywords people use to find and buy products/services such as yours) such as:
- CRM software
- CRM tools
- Customer relationship management solutions
As well as educational keywords. These are words your target customers use to look up information around your product (or the product’s use-case).
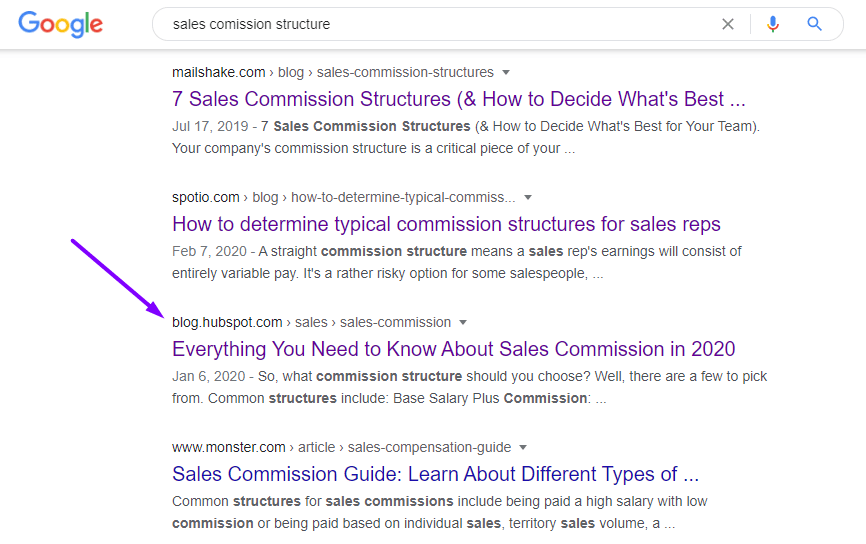
For example, a VP of sales looking up information on sales commission structure.
While your CRM doesn’t have anything to do with sales commission structure, there’s a good chance that anyone looking up this topic is starting a new sales team (and hence, is going to need a CRM).
If you actually Google “sales commission structure,” you’re going to see that HubSpot (a CRM software) is one of the top ranking results:
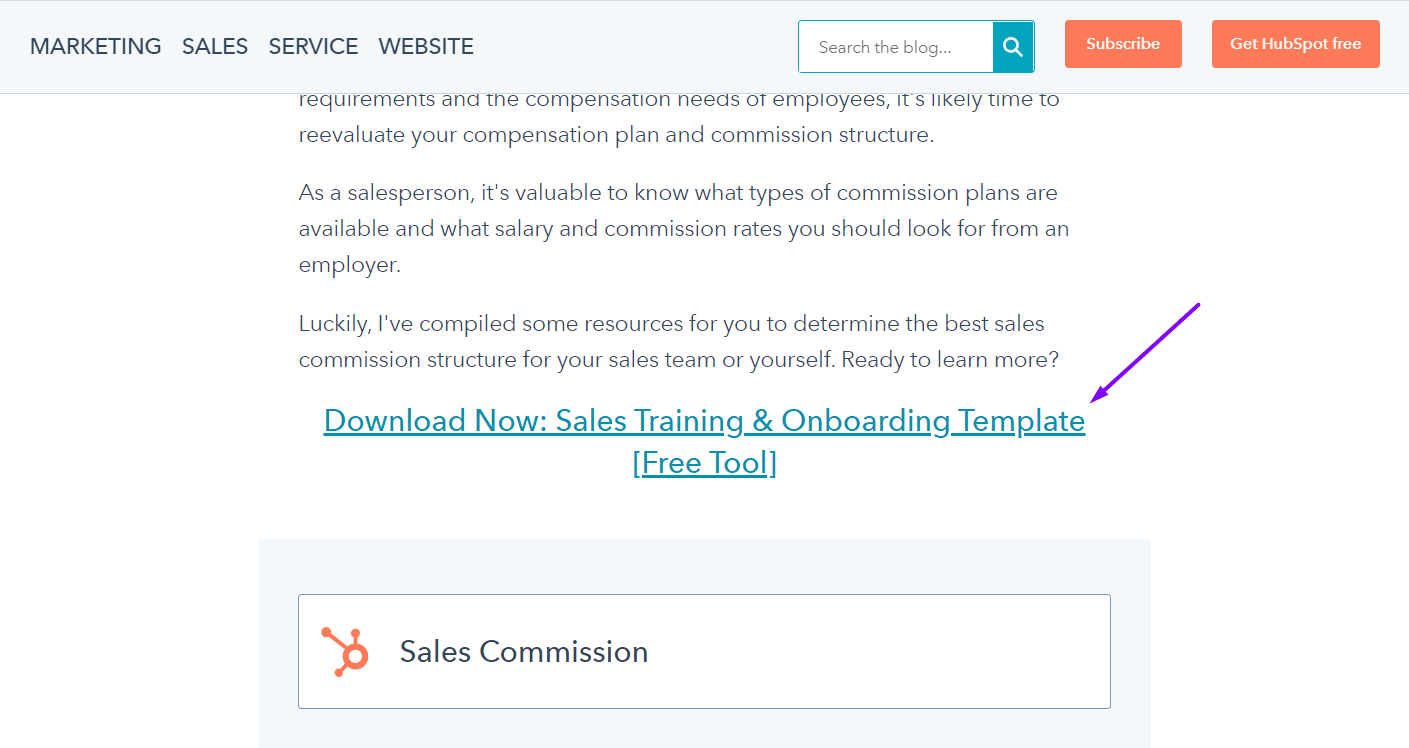
If you open their blog post, you’ll see that that are trying to capture your email through an opt-in (sales training template):
If you do opt-in, they’re going to eventually upsell you their CRM.
A good SEO strategy targets both direct intent and educational keywords.
B2B vs B2C SEO
If you’ve done SEO for a B2C business, you’ll find that B2B SEO does actually differ.
Some of the most blatant differences between the two are:
- B2B SEO is all about targeting decision-makers in organizations. B2C, on the other hand, can mean that your target audience is literally anyone, depending on the niche.
- B2B keywords tend to have significantly lower search volume than B2C. E.g: fewer people look for “enterprise BPM tools” than “how to make a resume.”
- On the other hand, ranking on B2B keywords can have a significantly higher ROI than B2C.
- From our personal experience, B2B SEO tends to be easier than B2C in most niches due to less competition.
Want to learn more about the differences between B2B and B2C marketing? Check out our B2B marketing guide.
The SEO Formula
This is where we talk about SEO top-down. We’ll give you a general run-down on how it works, and then go into the nits and grits in the next section.
The formula to achieve good rankings is as follows:
(1) Technical SEO + (2) on-page SEO + (3) high-quality content + (4) backlinks + (5) continuous improvement = Good rankings
Here’s how each part of the equation plays their part:
(1) Technical SEO is the foundation of your SEO. If your website doesn’t follow Google’s best practices, your rankings site-wide will suffer.
(2) On-page SEO. If your pages aren’t optimized around a keyword, they won’t get good rankings.
(3) The quality of your content is one of the most important factors that determine whether you rank or not. If your content is 10x better than everything that currently ranks, you’re going to get good rankings even if you don’t get any backlinks.
(4) Backlinks (i.e. links to your web pages) are (usually) the final and most important factor on whether you’re going to rank or not.
In an “end-game” niche (that’s where everyone knows what they’re doing, and is investing heavily in SEO), everyone has amazing content. In cases like this, what determines the order of rankings are backlinks.
Finally, (5) Continuous improvement. With SEO you can never stop improving, optimizing, testing, and iterating, over and over again.
Our B2B SEO Process
Now, let’s talk about the “how” of B2B SEO - what does “doing” B2B SEO involve, and what are the day-to-day tasks you’ll need to do?
Most SEO guides you’ll read on the web are way too much theory and not enough practice. So, to help change that, we’re going to stick 100% to practical work.
Here’s the EXACT process we use to grow clients to 2,000,000+ monthly organic traffic.
We’ll split up the process into several stages, including:
- Site Speed Improvement. Making sure that your website is as fast as possible and satisfies Google’s Core Web Metrics (and yes, most of the time, this DOES impact your rankings).
- Technical and On-Page SEO. Ensuring that your web pages follow Google best practices.
- Keyword Research. Finding phrases people use to search for topics around your business.
- Creating SEO Landing Pages. Creating pages meant to rank for direct-intent search keywords.
- Quality Content. Writing articles and web pages optimized for specific keywords.
- Ongoing Link-Building. Getting backlinks to your web pages.
- Interlinking. Regularly interlinking all your web pages, ensuring high website engagement metrics.
- Ongoing SEO Work. All things you’ll need to be doing on a regular basis.
Stage 1 - Site Speed Improvement
As of May of 2020, Google rolled out its newest ranking algorithm update (which will take ~1 year to take effect).
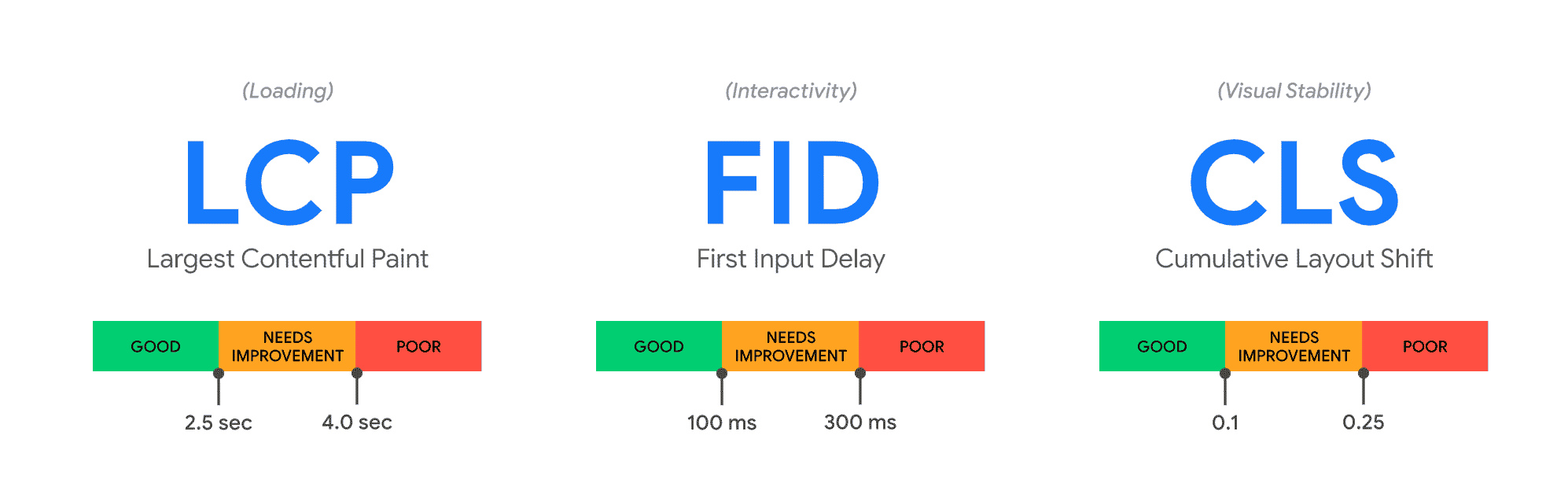
This Core Update introduces 3 new “website health” metrics, called the Core Web Vitals.
Because this might sound like gibberish to some people, we made a simple table to explain what each metric represents.
| Metric | Name | GOOD results | Layman terms |
| LCP | Largest Contentful Paint | < 2.5s | Measures loading performance |
| FID | First Input Delay | < 100ms | Measures page interactivity |
| CLS | Cumulative Layout Shift | < 0.1 | Measures page visual stability |
While we can’t teach you everything that needs to be optimized in order to achieve the above GOOD results, we’ve compiled a general checklist that can help!
Some things you can do to improve site speed are as follows:
- Resizing your images with Javascript or CSS
- Lazyload images on your website
- Enable Gzip compression
- Minify JS, CSS, and HTML
- Make your website mobile-friendly
Or, if you’re using WordPress, you can use the WP Rocket plugin and it’s going to do most of the work for you!
Want a more in-depth run-down on how to improve your website load speed? Grab our checklist here, and forward it to your IT team!
Stage 2 - Technical & On-Page SEO
The second step in doing B2B SEO is ensuring that your website is following Google’s best practices site-wide.
Meaning, your website should be technically sound, and all your web pages should follow on-page SEO best practices.
The on-page part is relatively straightforward: if you’re using WordPress, download RankMath, and optimize all of your web pages with it.
This includes mentioning the right keyword on each page, adding meta descriptions to all images, etc.
Not using WordPress? Here’s an on-page SEO checklist.
Technical SEO, on the other hand, is a bit more complicated. If you have a tech team, feel free to just give them the following technical SEO checklist:
- Create a Google Search Console account if you don’t have one
- Create a sitemap.xml file and submit it to GSC so your pages start getting indexed.
- Optimizing site architecture - ensure that the crawl depth for every page on the website is less than 4
- Use alt text on all images - try to include the keyword in the alt text whenever relevant
- Make sure that only one version of your website is indexable. Ensure that staging pages are NOT indexed by Google
- Make sure that you don’t have any duplicate pages
- Ensure that your website is accessible by crawlers
- Use structured data.
- Upload a robots.txt file
- Make sure your text to HTML ratio is above 40-50%.
Stage 3 - Keyword Research
Finally, now that we managed to get past all the technicalities, it’s time to talk about keyword research.
Keyword research is the act of finding the phrases your target audience uses to look for your business (or information around the problems you solve) and figuring out how to rank for them.
So for example, let’s say you have an Employee Onboarding Software.
Some keywords people can use to Google you are:
- Employee onboarding software
- Employee onboarding tools
- HR tools
- HR software
- Employee offboarding
On the other hand, your target audience can also be searching on Google for informational keywords like:
- Employee onboarding checklist
- How to onboard employees
- Employee orientation
And so on, you got the point
During keyword research, you need to find both types of keywords - direct intent (keywords used to find your software), as well as informational (keywords used to find information).
One of the most common mistakes newbies make with keyword research is targeting the same keyword in several variations. This leads to keyword cannibalization.
For example, the following keywords are all actually the same keyword - you don’t have to make 3 pages and try to rank for each of them:
- Small business accounting apps
- Best small business accounting apps
- Best small business apps for accounting
Creating a Keyword Sheet
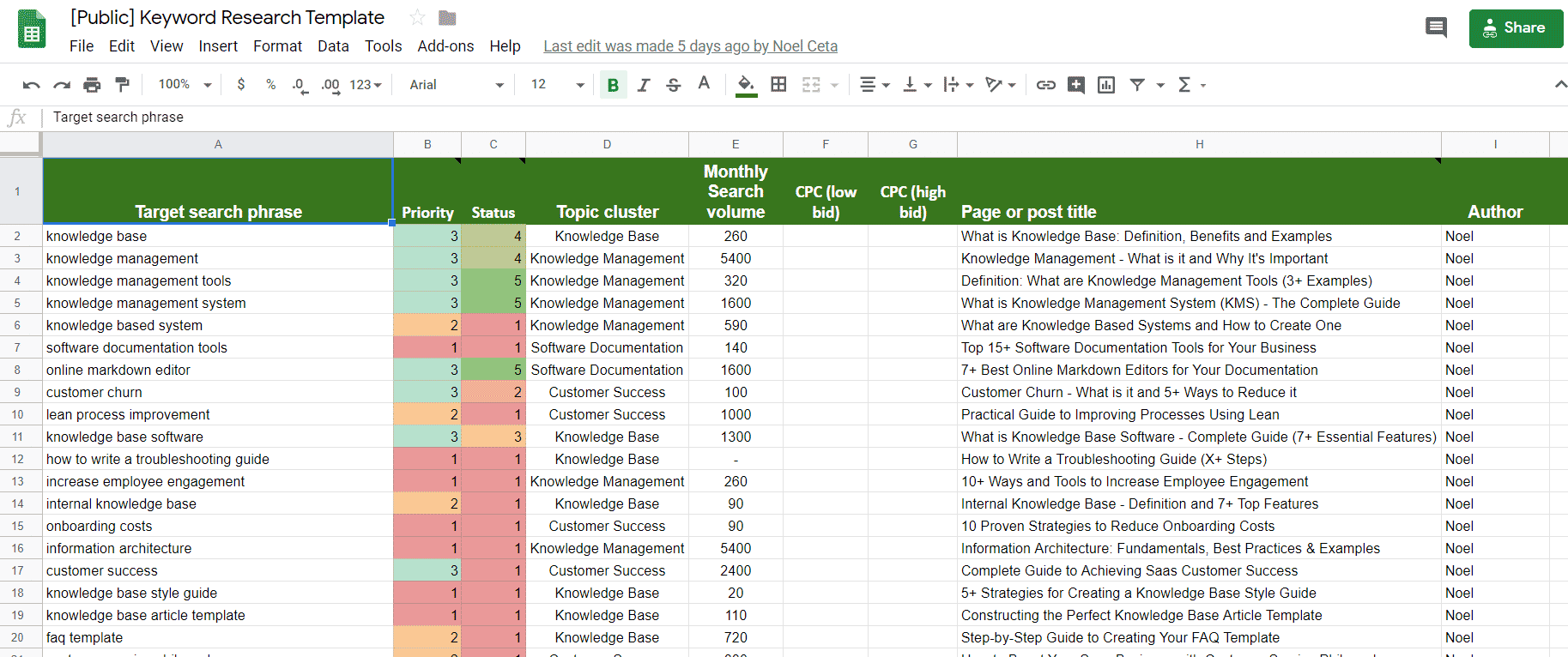
To get started with your keyword research, step #1 is to create a keyword sheet. This is where you’ll coordinate all your content marketing and SEO operations, as well as keep track of the keywords you’re targeting.
So, grab our template here, and start filling it in.
Here’s what the sheet should contain:
- Target search phrase. I.e. keyword you’re targeting.
- Priority. We usually divide keywords into 3 priorities:
- High-priority keywords. These keywords are high search-volume, low-competition, high buyer-intent, or all of them at the same time.
- Mid-priority keywords. These are the OK keywords, which we focus on once we’re done with the high-priority stuff.
- Low-priority keywords. Low volume, low-conversion, or just extremely hard to rank keywords
- Status. What’s the status of the article?
- 1 - Idea phase
- 2 - Writer is going to focus on this article for the week
- 3 - The article is a work in progress
- 4 - The article is being edited
- 5 - The article is finished and already published on the blog
- Topic cluster, or the category of the blog post.
- Monthly search volume. Pretty self-explanatory. This helps prioritize which keywords to target first.
- CPC (low & high bid). Cost per click you’d be paying if you were advertising for this keyword. The higher the CPC, the more your competitors are willing to bid for this keyword. Meaning, this keyword probably converts well.
Direct-Intent Keywords
Once you’ve got the keyword sheet up, it’s time to populate it with keywords.
We usually start with direct-intent landing page keywords (ones used to look for your product/service), and then move on to informational ones.
For these keywords, you’re going to be creating landing pages, instead of articles or blog posts.
So here, start off by listing out your main products/services.
E.g. if you’re a B2B sales & outreach agency, for example, you’d include:
- Sales
- LinkedIn outreach
- Email sales
Make a complete list of the keywords, so you’re as comprehensive as possible.
Then, transform these keywords into direct-intent keywords one-by-one.
E.g. “sales” would be:
- Sales agency
- Sales firm
- Sales consulting firm
And any other variation.
Once you’re done with all the products/services, your list should be pretty comprehensive.
Informational Keywords
Finding informational keywords is a bit harder, and can take a long time.
Here, we recommend you start with competitive research.
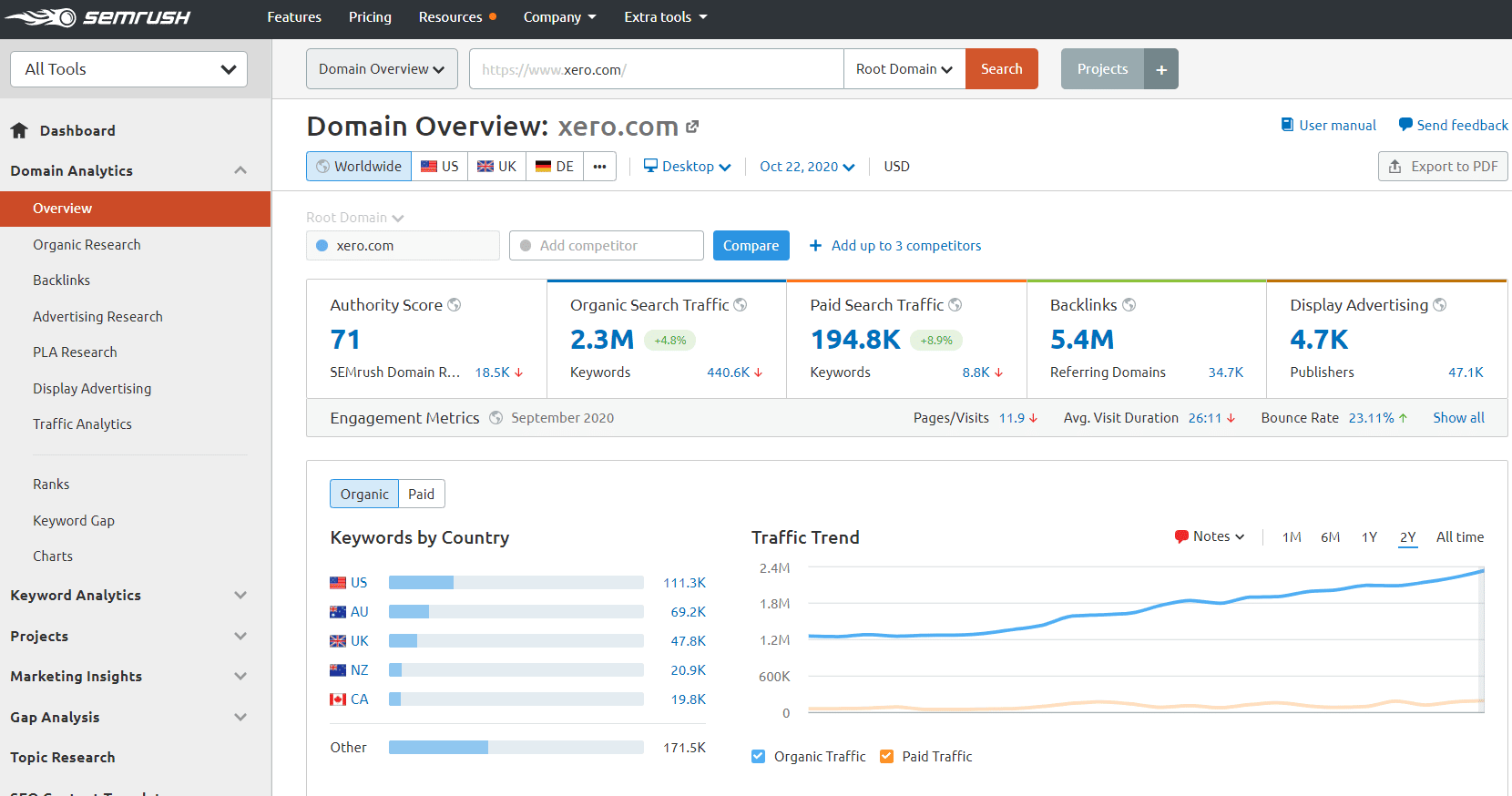
Get an SEO tool like SEMRush, and run your top 3 SEO competition (competitors with good SEO rankings) through it.
E.g. if you’re selling accounting software, your competition would be QuickBooks, Xero, etc.
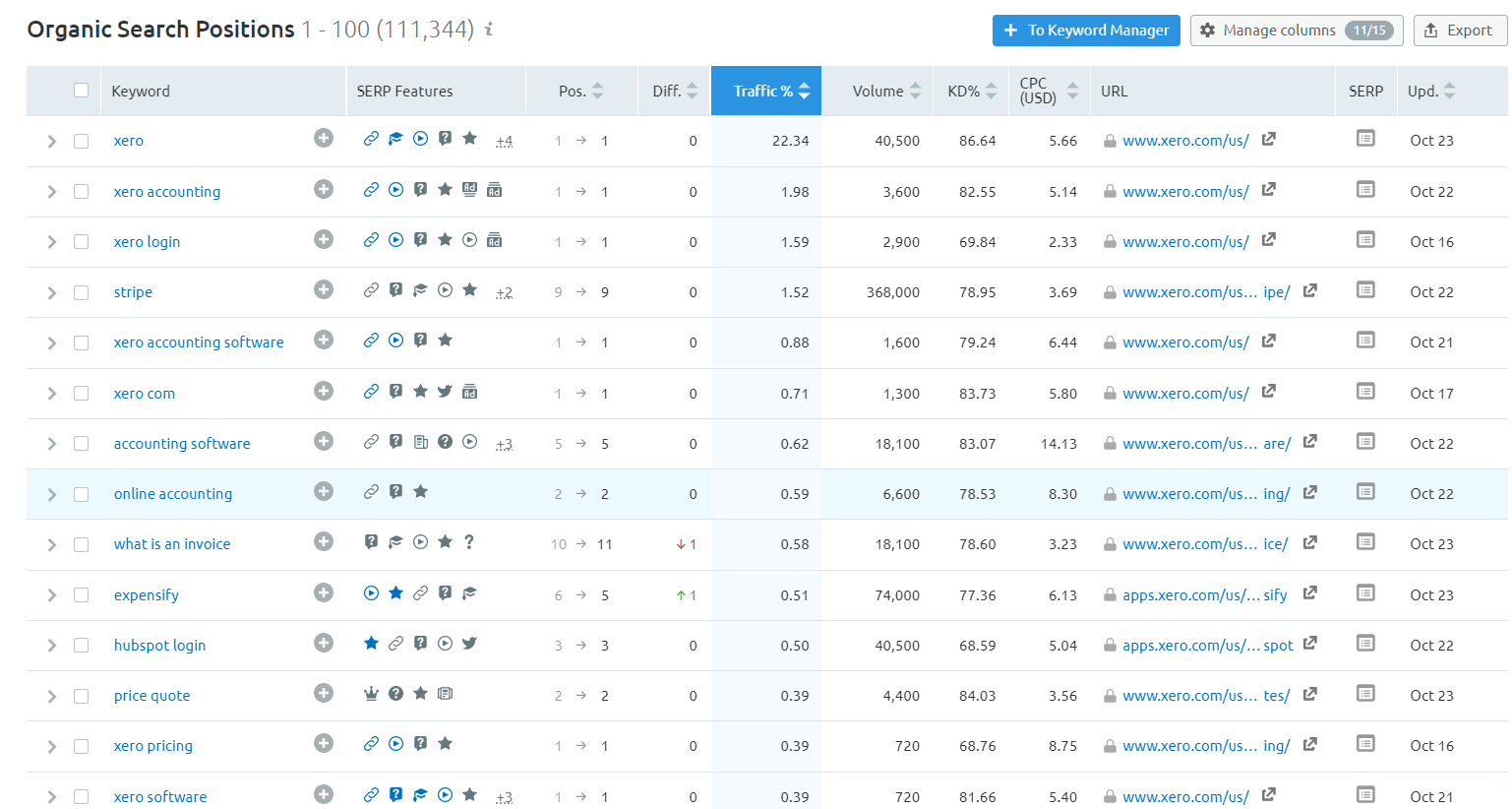
Now, you go through each of the competitor’s keywords, and extract them into your keyword sheet.
You keep doing this until you have around 200 keywords in total.
At this point, you can already stop and move on with the next step (i.e. creating landing pages and articles meant to rank for these keywords). Working with our clients, we usually stick to 200 keywords as a start, and when we cover them, we expand the keyword research on-the-go.
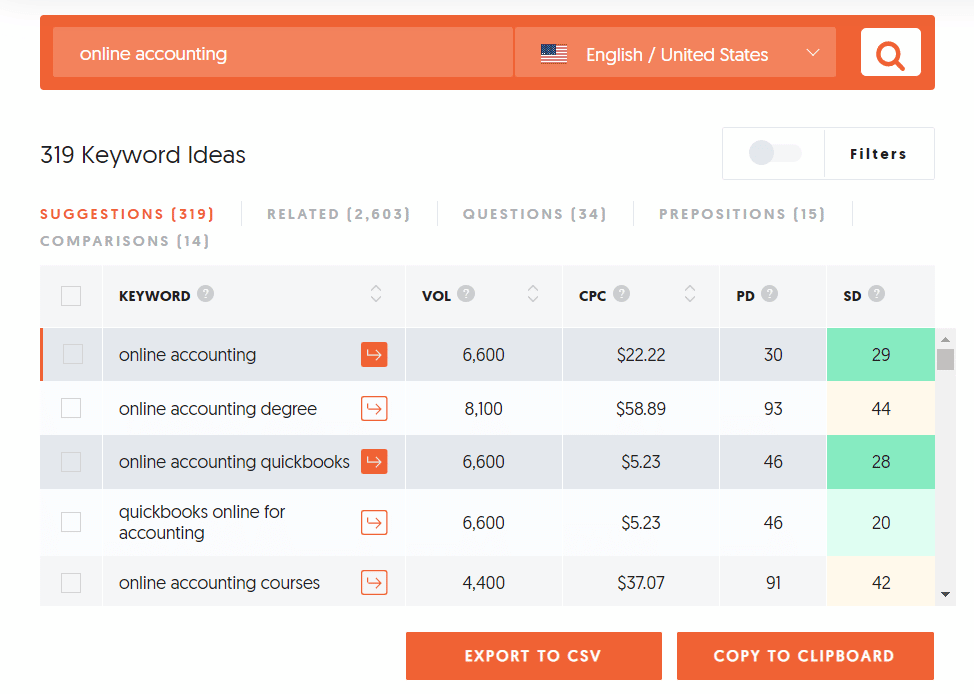
If you want to make the sheet as comprehensive as possible right now, though, you can do it using UberSuggest.
The way this works is, you take one of your high-volume keywords, run it through UberSuggest, and it’s going to give you a list of all associated keywords.
Pick up any of the keywords that seem relevant, and then just input another keyword from your sheet, until you manage to cover all possible keywords in your niche.
Stage 4 - Create B2B SEO Landing Pages
At this stage, we create the landing pages for direct-intent keywords.
The process here is relatively straightforward. First, pick one of the direct-intent keywords you found in stage #3.
Then, depending on the keyword, you’d want to create 2 types of landing pages:
- Generic Landing Page Template. If you’re targeting keywords that actually mean the same thing (e.g. sales software, CRM software, etc.), you can just take your homepage as a template, and re-create it as a landing page tailored for the given keyword. All you have to do is change the URL slug (make it the keyword you want to rank for), sub-headings, headers, re-word the copy on the page, and you’re good to go.
- Unique Landing Page. On the other hand, if you’re targeting keywords with different use-cases (e.g. workflow management software VS project management software), you’d create a completely custom landing page.
For a practical example of what an SEO landing page looks like, you can check out our SaaS Marketing Agency page.
Once you are done with the landing pages, just use RankMath to optimize it for the respective keyword, and you’re good to go.
Yep, it’s that simple.
Now, all you have to do is build links to the page and interlink it through the rest of the website (we’ll explain how this works in a bit).
Stage 5 - Create Quality B2B SEO Content
Once you’ve got the landing pages down, it’s time to create content targeting the informational keywords.
The SEO content creation process is done in 2 parts:
#1. Creating the Content Outline.
This is where you create a content outline for your writer (or for yourself - it still helps!).
An outline looks something like this:
And the purpose for it is to give the writer a direction on what they need to write in order for the content to rank.
See, unless you’re working with a writer that’s also an SEO specialist, you can’t just tell them to knock themselves out and write whatever.
Chances are, whatever they do won’t rank.
You need to tell them exactly what they need to write in order for this article to rank on Google.
So, how can you do this?
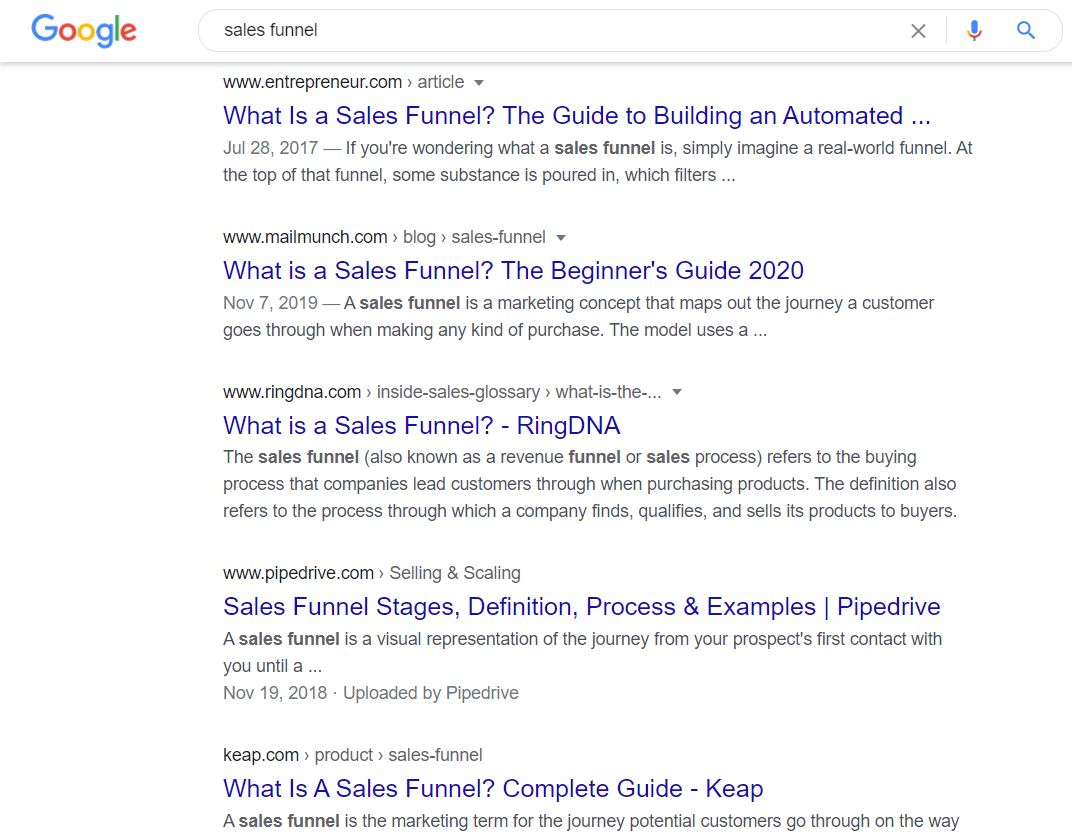
First, Google any given keyword. Let’s say, for example, you’re selling sales training to organizations, and want to rank for the keyword “sales funnel.”
You need to go through each of the articles ranking on the keyword, and use them as inspiration to come up with a structure for your article.
You’ll see that most ranking articles have a similar structure that looks something like this:
- Introduction [h2]
- What is a Sales Funnel [h2]
- Understanding the Sales Funnel Stages [h2]
- #1. Awareness [h3]
- #2. Interest [h3]
- #3. Decision [h3]
- #4. Action [h3]
So, what you can take from this is that your article should be structured in a similar way (if you want to satisfy the Googler’s search intent and rank with your article, of course). You need to explain what a sales funnel is, and what each stage of the funnel means.
So, you’d slap that on your outline.
Then, you need to think how you can add additional value to the topic. How will your article differentiate (and one-up) whatever is already ranking?
Some ways you can do this include:
- Add more in-depth information on the topic. E.g. you could include what type of marketing initiatives can help drive a sales prospect from one stage to another.
- Add more practical examples. Everyone likes a practical article they can instantly turn into something useful (vs reading about boring theory).
- Make the article more comprehensive. Add additional information that others haven’t covered.
- Add results-based case studies.
- Make the article more visually appealing and readable. You can do this by adding more images, visuals, etc.
Whatever you decide, add them to your outline.
Finally, you need to decide on how much word count the writer should aim for. There’s no golden rule on what works here, but we usually recommend the following:
Make the article as comprehensive as you possibly can. If that means hitting 2x your competitors’ word count, go for it!
If, however, your competitor’s articles are already as good as they can be, you can just stick to the same length.
Usually, you’d want to aim for 1,000 to 5,000 in word count. Anything less is not comprehensive enough, and anything more can be too comprehensive.
Of course, there are exceptions to this, but this is the general rule.
#2. Creating Amazing Content
Once you’re done with the outline, it’s time to get to writing (or give the outline to a writer, anyway).
At this stage, all that’s left is for them to write really, really good content.
We’ve had a lot of our clients ask, “what’s good writing, exactly? How can I know if a content piece is good or bad?”
Here’s what you should focus on if you want to create quality content:
- Write for your audience. Keep in mind who you’re writing for. If your audience is a suit-and-tie lawyer, for example, you’d want to stick to a formal and professional tone (and avoid Rick and Morty references). If you’re writing for 19-year-old hipster skateboarders, though, you can go for a casual, humorous tone.
- Never, ever, fluff. After writing each sentence, ask yourself “so what?” If you removed this sentence, would the article lose any value? If the answer is “no,” you probably don’t need the sentence in the first place.
- Make your content practical. Good content is practical - no one cares about the theory. Include practical examples, real-life case studies, and so on.
- Keep your audience’s knowledge in mind. If you’re writing on a beginner accounting topic, you need to keep in mind that the reader probably doesn’t know what credit/debit is, so you’d have to explain the very basics. On the other hand, if you’re writing about the ins and outs of corporate finance, you can probably skip the basics.
- Create writer guidelines to make sure that your writers know what exactly, you expect from them. Or, just steal ours!
- Write for a 6th grader. When writing content for the internet, you need to make sure that it’s readable by just about anyone. No one wants to decipher shakespeare-level writing in their free time & Google for word definitions. They want to get the info quick and easy.
Don’t have a qualified writer on-hand? Learn how to hire SEO content writers with our guide.
Stage 6 - Ongoing Link-Building
Link-building is the act of getting other website owners to link to your articles and web pages.
In competitive industries where everyone’s already following most SEO best practices, what really decides the rankings are the backlinks.
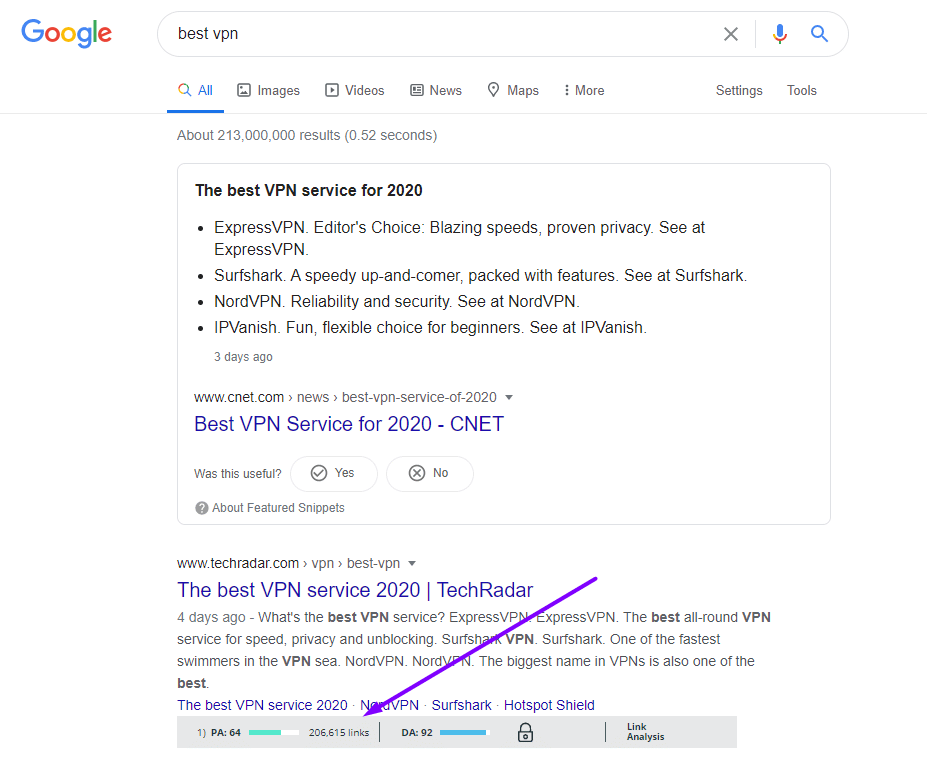
If you Google “Best VPN,” for example, you’ll see that the #1 ranking article has over 200,000 backlinks.
So what that means is, even if you create the best article on VPN services that was ever written, it won’t see the light of day without a ton of links.
Even in non-competitive industries, backlinks are what determine how long it’ll take for your web pages to rank.
An article that would rank in 9 months without backlinks can rank in 4 with quality backlinks.
There are a TON of link-building strategies out there, so we won’t cover every single one of them here.
That being said, some of the most popular link-building tactics include:
- Broken Link-Building. You find articles with broken links on similar topics to yours, and reach out to the website owner, letting them know about the broken link, and proposing to replace it with yours.
- Guest Posting. Reaching out to popular blogs in your niche and asking them to publish your guest posts.
- “Linkable Asset” Link Building. Creating super useful resources and promoting them all over the web.
- Skyscraper Technique. This one’s a technique created by Brian Dean from Backlinko. It involves finding linkable resources, creating something even better, and promoting them to people who linked to this resource before.
Want a complete list of link-building tactics? Check our Brian Dean’s article.
At Apollo Digital, we have our own spin on link-building. Instead of reaching out to website owners and asking for links at scale, we create epic content, promote it on the web, and land links and traffic that way.
Want to learn more? Check out our content marketing case study. By promoting one single article, we managed to get insane results like:
- 10,000 traffic in one week on a fresh blog
- 15+ leads
- 50+ links
- $50,000 in generated revenue
Stage 7 - Internal Linking
Internal linking, or interlinking, is the process of linking your web pages and blog posts together.
Proper interlinking can have a significant impact on your Google rankings for 2 reasons:
- The more internal links any given page has, the more authoritative it is in the eyes of Google. It assumes since a specific page has a lot more links than others, it’s probably important.
- Internal links help improve traffic retention. I.e: if someone lands on one of your articles, and then finds another relevant article through an internal link, they end up sticking around longer on your website (which is a ranking factor for Google).
- Proper internal linking makes your content easier to access by Google’s crawlers.
We usually do interlinking in 3 different ways.
First, we make sure that our writers link to relevant existing content in any article they’re writing. E.g: if they’re writing about a SaaS topic, we ensure that they link to all our existing SaaS articles.
Then, whenever a new article is published, we go through our existing content on the same topic, and link to the fresh post.
Finally, we also do 3-4 interlinking initiatives per year. Every few months, we go through all of our blog posts, and manually make sure that every article links to as many relevant pages as possible.
Stage 8 - Ongoing SEO Work
SEO work is never done - you don’t just wake up one day and realize you’re getting everything you want from Google, close shop, move to a beach in Thailand, and sip on mojitos for the rest of your career.
There are a ton of things you can be doing on an ongoing basis to ensure that you’re getting the most out of your SEO:
- Regularly keep track of the CTR on your ranking articles, and ensure that your headlines are clickable in order to drive as much traffic as possible. If a given article has a lower CTR than you’d expect, you can A/B test different titles. For more on CTR optimization, check out this article.
- Track which articles rank, and which ones don’t. For the ones that don’t look into each individual case, and figure out why (and fix it accordingly):
- Is the content not as comprehensive as it can be?
- Did the writer miss the point with the article?
- Is the article not interlinked well with the rest of your web pages?
- Does the article not have enough links?
- Disavow spammy or PBN links coming to your website to ensure that you’re not at a risk of being penalized by Google.
- Ensure that you don’t have any broken links on your website.
- Establish relationships with other bloggers, and collaborate with them on link-building.
B2B SEO Case Study - 0 to 200,000 Monthly Organic Traffic
We get it - it’s one thing to read about a topic, and it’s something completely different to implement it.
To help you really understand the entire B2B SEO process, here’s our case study on how we grew a B2B workflow management SaaS from 0 to 200,000 monthly organic traffic.
And this wasn’t just vanity traffic, either. We managed to rank for some very competitive, high-CPC keywords (20 USD per click and above!).
Here’s exactly what we did:
- Audited the client’s keyword strategy and trimmed it to only what was really relevant. We only kept topics on process management and workflows, and cut out topics like SEO, marketing, etc.
- Found pages that were cannibalizing each other and merged them.
- Audited the client’s existing content and split them between Good, Salvageable, and To-Delete.
- Established new writer guidelines and pushed the writers in a new direction.
- On an ongoing basis, we interlinked all articles to increase site stay time metrics.
- Improved the blog visuals and started using custom CSS boxes.
- Kept track of CTR for all pages & optimized headlines.
Want to get the whole story? Read the complete SEO case study here.
B2B SEO FAQ
#1. How long does it take for B2B SEO to bring traffic?
It really depends on a variety of factors, including:
- How high your domain authority is. I.e: how many quality backlinks you have, how old your website is, etc.
- Competitiveness in your niche. If a competitor’s page on a given keyword has thousands of backlinks, you’ll have to really try hard to get on the same level.
- How well-written the content in your niche is. I.e: are there low-quality articles ranking for your keywords, are all of them super high-quality long-form?
If your niche isn’t all that competitive, and you have a website that isn’t completely fresh, you can expect rankings within 6 months to a year.
On the other hand, if your website is completely new, or your industry is very competitive, getting results can take anything from a 1 to 5 years.
#2. Is B2B SEO the right choice for my business?
Depends. SEO is a very long-term strategy. If you want to get new users tomorrow, then SEO might not be the right choice.
However, if you’re willing to invest in your growth for 1-2 years, then yes, you should go with SEO.
On the same note, you should also consider that if you have a very niche target audience, it might be better to do direct outreach or sales instead.
E.g. you’re selling enterprise software, and there are ~300 max target customers worldwide, you’re better off just reaching out to them directly.
If B2B SEO doesn't work for your business, check out these 11+ other B2B marketing strategies.
#3. Is SEO important for B2B?
SEO is very important for B2B companies. You can use it to drive leads on autopilot, make your brand memorable, and grow your business without spending thousands on paid advertising.
Most B2B high-intent keywords are very expensive when it comes to running ads. You can expect to pay anything between 10 and 50 USD for a click.
#4. How does SEO affect your business?
SEO can have a very large impact on your business. If you dominate the SEO space of your niche, you can expect hundreds or thousands of new leads every month (without any paid advertising).
#5. Is SEO dead?
Obviously not. The “SEO is dead” articles are just pure clickbait. If you know what you’re doing, SEO can be one of your top marketing channels in 2021.
#6. Should I use blackhat techniques or PBNs?
Unless you have a time machine and can go back to the 2000s, the answer is a clear NO.
In 2021, blackhat SEO is way too high risk and low reward.
Imagine this - you spend 1-2 years building up your Google rankings with a PBN. You spend tens of thousands of dollars buying PBN links, and even more on quality content.
You get your rankings, you’re driving leads and SEO is finally paying off…
...Right until Google finds your PBNs, and penalizes your website, bringing you back to square one.
#7. What are the best SEO blogs where I can learn more on B2B SEO?
Some of our favorite SEO blogs include:
#8. What's the difference between B2B SEO & content marketing?
While content marketing is part of SEO, the reverse is not necessarily true. B2B content marketing can drive both traffic and leads without getting any rankings on Google.
Want to learn more about content marketing without SEO? Check out our B2B content marketing guide.
Work With Apollo Digital - A B2B SEO Agency
Unless you’re already an SEO expert, getting started with B2B SEO can be really tough.
You’ll need to:
- Understand the ins and outs of writing high-quality content
- Master the art of outreach to start getting backlinks
- Create a high-level SEO strategy and execute it
If all that sounds like too much to handle, we can help.
Apollo Digital is a B2B SEO agency, and we’ve helped several companies such as yours set up an SEO strategy and execute it from the bottom-up.
Whether you’re looking for a consultant to make sure that you’re doing everything right, or an implementation partner to handle 100% of the SEO management for you, we can help.
Conclusion
Wow, you went through the entire 5k-word article!
At this point, you should know all you need to know in order to get started with your B2B SEO initiative.
Now, all we can say is, best of luck!
And of course, if you need some help with your SEO, reach out to us for a free consultation.